The KL-Emotor Motor Emulation System consists of four subsystems: Test Management Subsystem, Real-time Simulation Subsystem, Power Interface, and Signal Interface.
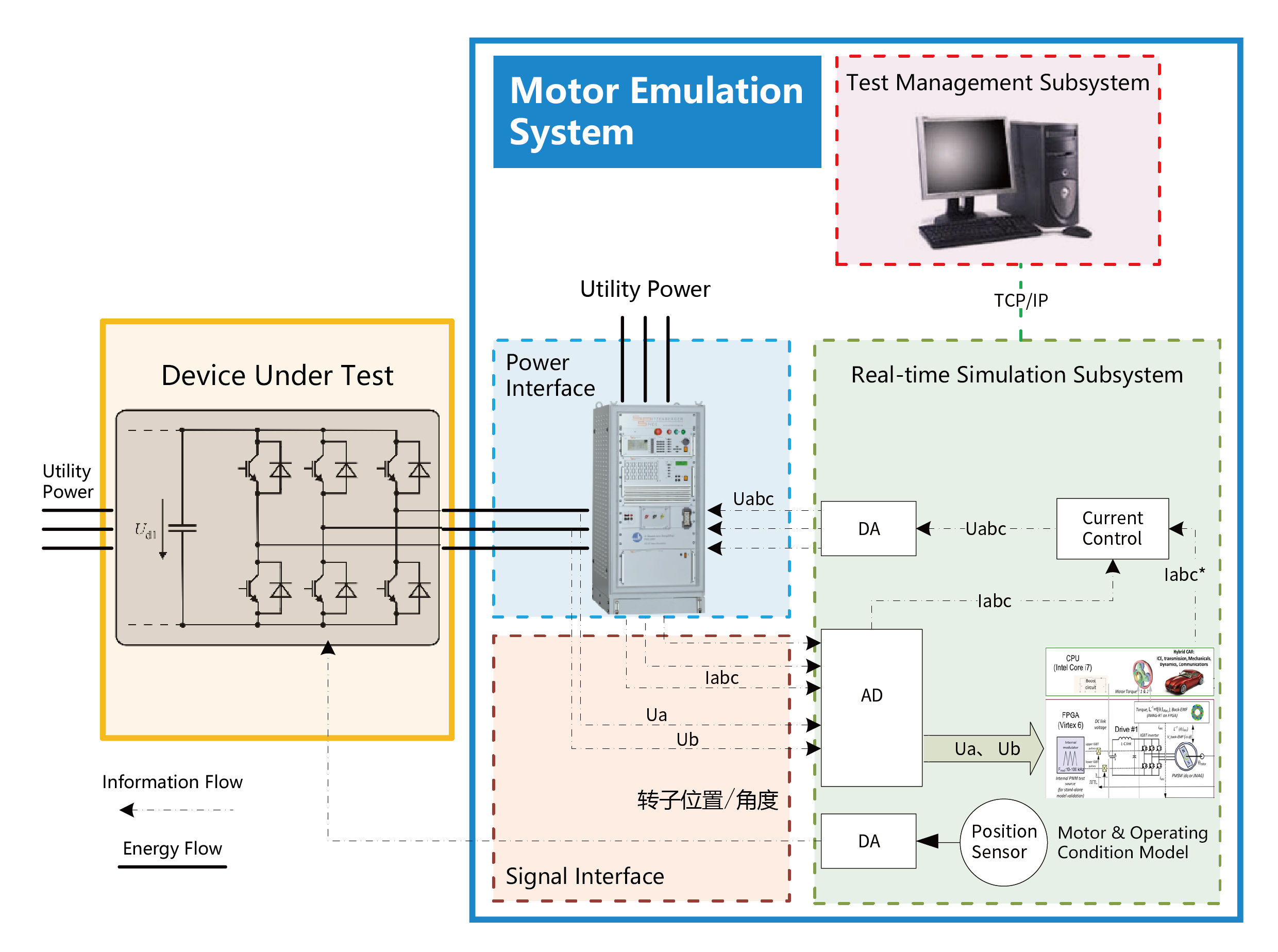
The Test Management Subsystem is the host computer system. It controls the operation of the Real-time Simulation Subsystem via ethernet and runs the specially developed software QuiK-Emotor for the KL-Emotor system. It performs functions such as motor model configuration, test management, automatic testing, data monitoring, data analysis, and data storage.
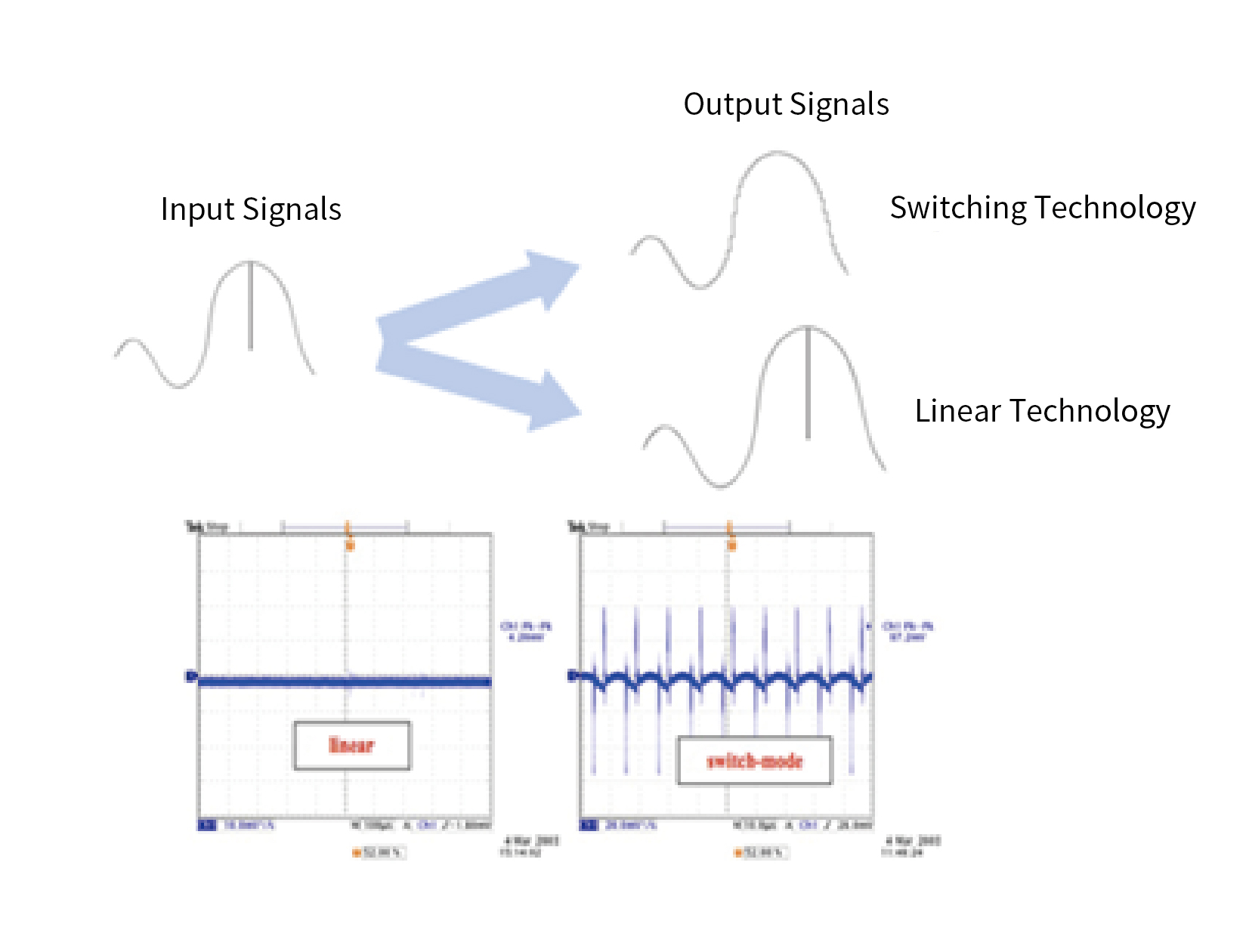
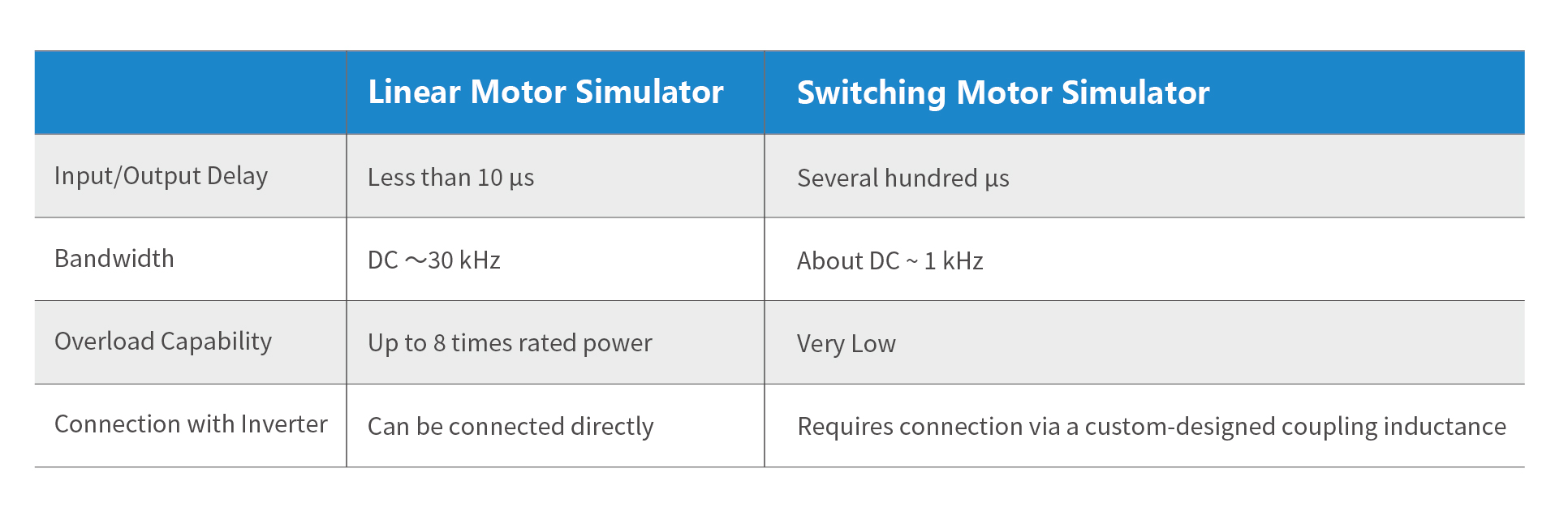
The Real-time Simulation Subsystem is the lower-level computer system and serves as the core of the entire system. It includes the RT-LAB OP5600 real-time simulator and various I/O boards. It must support real-time execution of system mathematical models and real-time I/O port configuration. By sampling the voltage and current signals output from the power amplification subsystem via I/O, it participates in solving the high-fidelity motor model to obtain the reference output current values Iabc*. These are then used by the current controller to generate voltage reference values for the power amplification equipment, ensuring that the voltage and current characteristics at the three-phase output match those of the simulated motor. Additionally, the solved results from the speed/position sensor model are output to the controller of the device under test via appropriate I/O boards, contributing to motor control. The solving in this subsystem can be performed using either the CPU or the FPGA according to user requirements. The CPU achieves a simulation step size of 10 μs, while the FPGA achieves a simulation step size of 250 ns, enabling simulation of motor harmonic back-EMF, cogging effects, three-phase asymmetry, and other phenomena.
The Power Interface establishes the power connection with the device under test. The Signal Interface samples the three-phase output voltage and current via sensors and feeds them into the Real-time Simulation Subsystem for model solving.
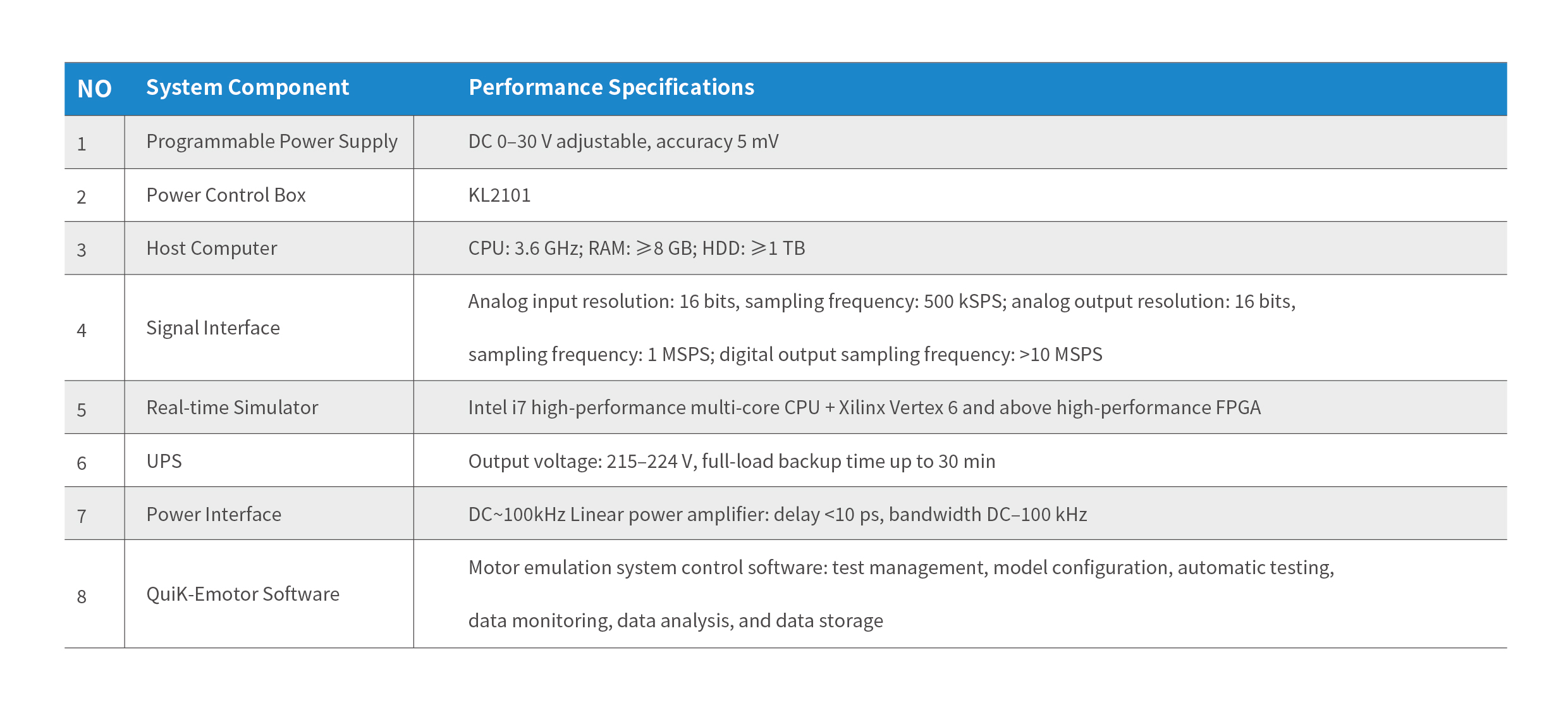
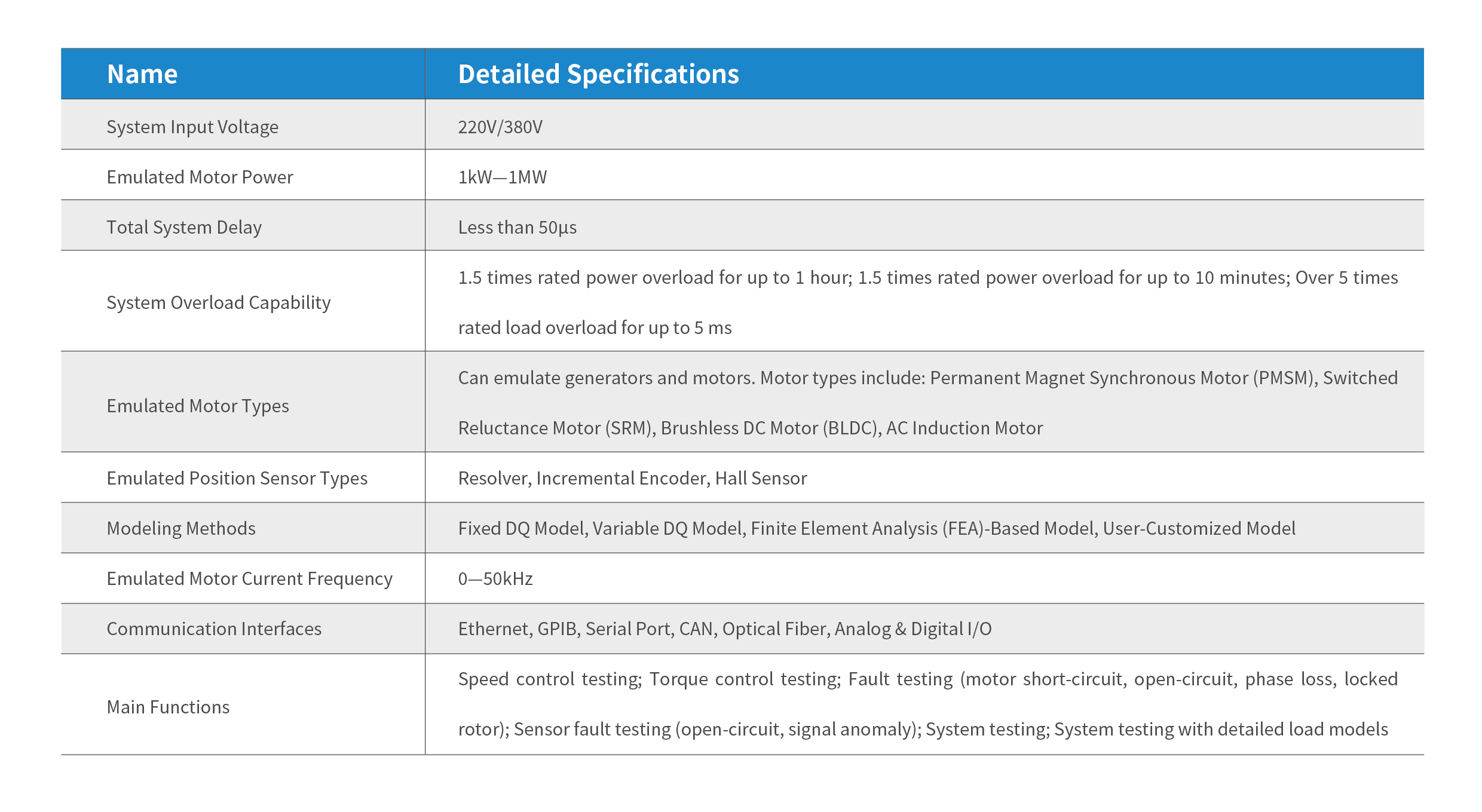
Detailed technical parameters of the KL-Emotor Motor Simulation System are as follows:
Electric motors play an important role in the development of modern industries, including aviation, aerospace, marine, power, and automotive sectors. Especially with the rapid advancement of technologies such as electric vehicles, wind power generation, locomotive traction, and marine electric propulsion, the design, development, and testing methods for various motors and motor controllers remain relatively limited for R&D personnel.
The traditional testing method involves building a motor test bench using a dynamometer as the load motor. The advantage of this method is high testing accuracy under conventional operating conditions. However, it also presents the following issues: (1) The test bench itself occupies a large area and is costly; (2) High-speed rotating mechanical components pose risks to testing personnel; (3) It cannot conduct tests under conditions such as high rotational speeds or electrical faults; (4) It imposes high control requirements on the load motor; (5) It is inconvenient to change the type or model of the motor under test.
Another prevalent testing methodology is Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) technology. It utilizes real-time simulation equipment to emulate motors, power conversion devices, and sensors (e.g., voltage/current/speed), enabling closed-loop interaction between physical motor control boards and real-time simulation models via I/O interfaces. This approach facilitates efficient development and validation of motor control strategies. However, since it only involves signal-level data exchange and excludes critical hardware components like drive circuits and power circuits, it cannot test a complete motor controller system. Rather, it constitutes Controller Hardware-in-the-Loop (CHIL) testing.
To address the problems of the methods mentioned above, KeLiang has developed the KL-Emotor Motor Simulation System using advanced Power Hardware-in-the-Loop (PHIL) technology. This system is tailored for testing various types of motor controllers or inverters across different fields and is a key piece of equipment for the future development and design of motors and motor controllers.
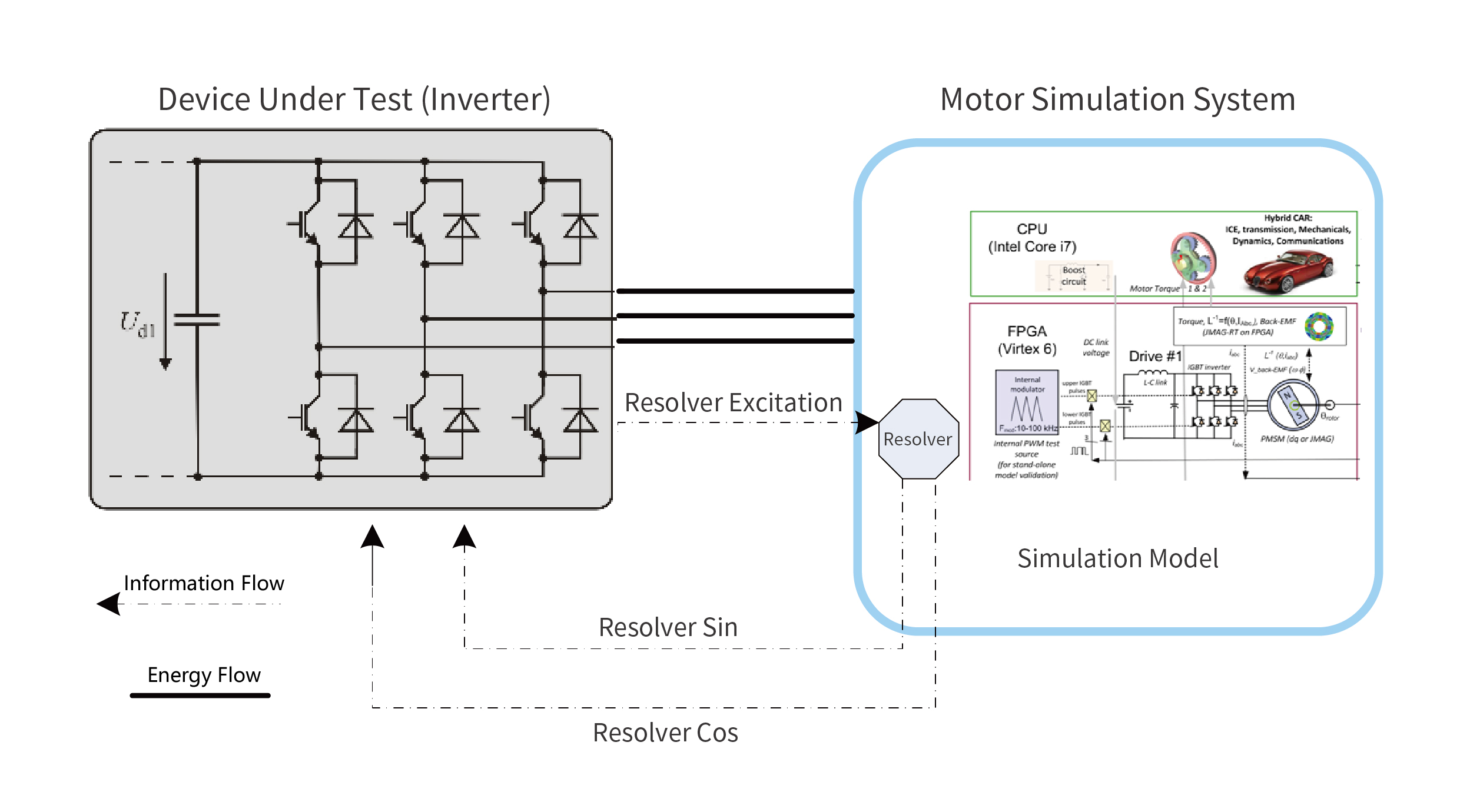
Motor Models
The motor models configured in this system include both CPU-based and FPGA-based models. Motor types encompass: Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) model, AC Induction Motor model, Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM) model, etc. Modeling methods include: Fixed DQ Model, Variable DQ Model, Finite Element Analysis (FEA)-Based Model, etc. Furthermore, motor models can be customized according to user requirements.